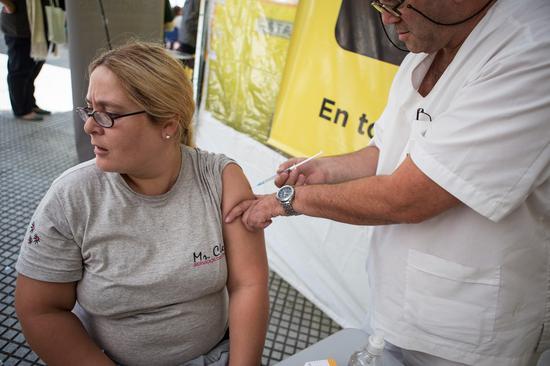
A woman receives a vaccine for Hepatitis B at a stand during a fair for basic services in prevention of disease in the context of the World Health Day's commemoration, in Buenos Aires, Argentina, on April 7, 2015. (Xinhua File/Martin Zabala)
World Health Organization (WHO) Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said Monday that the global prevalence of hepatitis B infections in children under five years of age has been reduced to less than 1 percent.
"New research led by WHO and the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine shows that together we have achieved the global target set in 2000 to reduce the prevalence of hepatitis B infections in children under five years of age to less than 1 percent by 2020," Tedros said at a virtual press conference on Monday.
"This landmark achievement means we will dramatically reduce the number of cases of liver cancer and cirrhosis in future generations," he said.
Tuesday is World Hepatitis Day. Tedros said an estimated 325 million people globally live with hepatitis B or C, and each year these viruses kill an estimated 1.3 million people.
According to the WHO chief, new drugs have transformed hepatitis C from a lifelong, deadly disease into one that in most cases can be cured in 12 weeks, but in many countries, the medicines remain expensive and out of reach for many patients.
At the same time, he added, progress is also being hampered by low coverage of the hepatitis B vaccine in some regions, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, where many children still miss out on the all-important vaccine dose at birth.
Caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis B is a liver infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic diseases, WHO said on its website.
The virus is most commonly transmitted from mother to child during birth and delivery, as well as through contact with blood or other body fluids, WHO said.