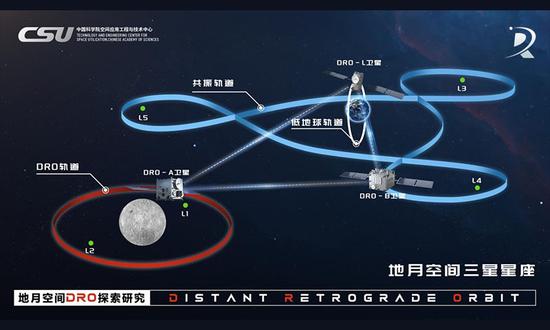
China has successfully established the world's first three-satellite constellation on the distant retrograde orbit (DRO) in the Earth-moon region of space, connecting them with stable inter-satellite measurement and communication links, China Central Television (CCTV) reported Wednesday, citing updates from program developer the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS.)
Such development has yielded variety of original scientific and technology outcomes, laying a solid ground for the country's future development of the Earth-moon region of space and frontier exploration of the space science, the CAS disclosed in the update.
Per the CAS, the Earth-moon region of space refers to the expanded domain extending outward from Earth's orbit, reaching up to 2 million kilometers from Earth. Compared to Earth's orbital space, its three-dimensional volume expands by more than a thousand times, the academy explained.
Developing and utilizing cislunar space holds tremendous strategic significance for lunar resource exploitation, long-term human habitation beyond Earth, interplanetary activities, and the sustainable exploration of the solar system, it added.
The CAS launched preliminary research and key technology development in this region in 2017. In February 2022, a pilot project was initiated to develop and launch three satellites to form a large-scale satellite constellation in the region of space, aimed at exploring the unique characteristics and application potential of the DRO.
The DRO-A and -B satellites were launched in March 2024, and entered their mission orbit on July 15 the same year, while the DRO-L was launched in February 2024 into a sun-synchronous orbit and began conducting experiments as planned. The three formed the constellation for the first time in August 2024.
The plan included DRO-A satellite permanently staying in the DRO, while the DRO-B satellite operates in Earth-moon space maneuver orbits, according to CAS' Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization (CSU.)
Chinese scientists have made significant breakthroughs in ranging fields since the set-up of the three-satellite constellation in 2024.
Building on years of research in Earth-moon region of space astrodynamics and space exploration, the scientific team proposed an innovative design concept: trading longer flight time for increased payload capacity and greater contingency margin. As a result, the satellites completed Earth-moon transfer and achieved low-energy DRO insertion using only one-fifth of the fuel required by traditional methods, marking the world's first successful low-energy insertion into a DRO.
This breakthrough significantly reduces the cost of accessing cislunar space, opening up new avenues for large-scale development and utilization.
The team also achieved another world-first by successfully verifying a 1.17-million-kilometer K-band inter-satellite microwave measurement and communication link, overcoming a major technological bottleneck in building large-scale constellations in cislunar space.
In terms of space science, the mission has also supported astrophysical research such as gamma-ray burst detection and trialed new technologies, including operating atomic clocks.
Moreover, Chinese researchers successfully validated a new space-based orbit determination system whereby one satellite tracks another, replacing traditional ground-based tracking. Using just three hours of inter-satellite measurement data, they achieved orbit determination accuracy equivalent to over two days of traditional ground tracking. This breakthrough significantly lowers the cost of orbit determination for cislunar spacecraft, paving the way for more efficient operations.
Wang Wenbin, a researcher at CSU, hailed that this achievement marks the first time internationally that orbit determination was verified using satellite-to-satellite tracking rather than ground stations.
"It's like turning a traditional ground station into a satellite and placing it in a low-Earth orbit," he explained. "This opens a new technical pathway for China's future cislunar and deep space exploration. It also provides an efficient solution for orbit determination, navigation, and timing across various cislunar orbits, supporting the future expansion of large-scale commercial activity in cislunar space."

















































 京公網安備 11010202009201號
京公網安備 11010202009201號