![Photo provided by the China National Space Administration on Jan. 3, 2019 shows Yutu-2, China's lunar rover, leaving a trace after touching the surface of the far side of the moon. [File photo: Xinhua]](http://image.cns.com.cn/ecns_editor/transform/20190516/MUK--fzikckp5228234.jpg)
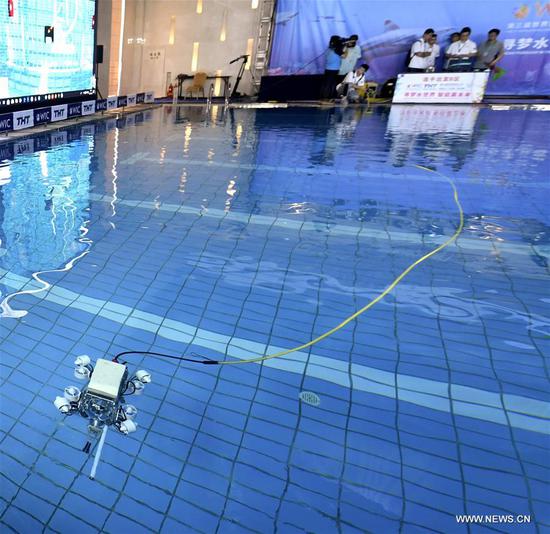
Photo provided by the China National Space Administration on Jan. 3, 2019 shows Yutu-2, China's lunar rover, leaving a trace after touching the surface of the far side of the moon. [File photo: Xinhua]
Measurements from China's Chang'e-4 mission to the far side of the Moon have revealed the presence of material from the lunar mantle at the landing site, according to a study published online Wednesday in the journal Nature.
The Chang'e-4 probe touched down at the Von Karman Crater in January 2019 and deployed the Yutu-2 rover to explore the South Pole-Aitken Basin on the far side of the Moon.
Previous global remote sensing missions from orbit have concurred with the idea that "the best candidate for excavating lunar mantle materials was the huge South-Pole Aitken Basin which, given its size, should have tapped into the mantle through the lunar crust", Patrick Pinet at France's Research Institute in Astrophysics and Planetology, told Xinhua through email.
The detailed structure of the Moon's mantle has eluded investigators for years. Scientists have focused their efforts on the impact craters as the events leading to their creation may have penetrated the crust into the lunar interior, excavating parts of the mantle and distributing them on the surface.
Based on the initial observations from Yutu-2's Visible and Near Infrared Spectrometer, a team led by researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences inferred the presence of low-calcium pyroxene and olivine minerals, which may originate from the upper mantle, on the surface.
They argued that this material was excavated from below the South Pole-Aitken basin floor by the nearby Finsen impact crater.
The lunar mantle's composition characterization is "a very important step to conduct", as it allows researchers to present better models of lunar interior evolution and "to address related questions about lunar magma ocean and its solidification/cooling", said Pinet, who also wrote an accompanying article commenting on the Chinese team's latest findings.
To further confirm the findings, it is still necessary to bring back a sample of the rocks to Earth for analysis, according to Pinet.