
Image captured by the satellite SDGSAT-1 shows a view of the Yangtze River Delta. China's recently launched Earth science satellite has sent back its first remote sensing images, according to its developer, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Using thermal infrared, low light level and multispectral imagers, the satellite captured images of multiple cities and regions, including Beijing, Shanghai, the Yangtze River Delta, Lake Namtso in Tibet, Aksu Prefecture in Xinjiang, and Paris in France. The satellite SDGSAT-1 is the world's first space science satellite dedicated to serving the U.N. 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The satellite was launched into space on Nov. 5. (Chinese Academy of Sciences/Handout via Xinhua)

Image captured by the satellite SDGSAT-1 shows a view of the Yellow River estuary. China's recently launched Earth science satellite has sent back its first remote sensing images, according to its developer, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Using thermal infrared, low light level and multispectral imagers, the satellite captured images of multiple cities and regions, including Beijing, Shanghai, the Yangtze River Delta, Lake Namtso in Tibet, Aksu Prefecture in Xinjiang, and Paris in France. The satellite SDGSAT-1 is the world's first space science satellite dedicated to serving the U.N. 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The satellite was launched into space on Nov. 5. (Chinese Academy of Sciences/Handout via Xinhua)
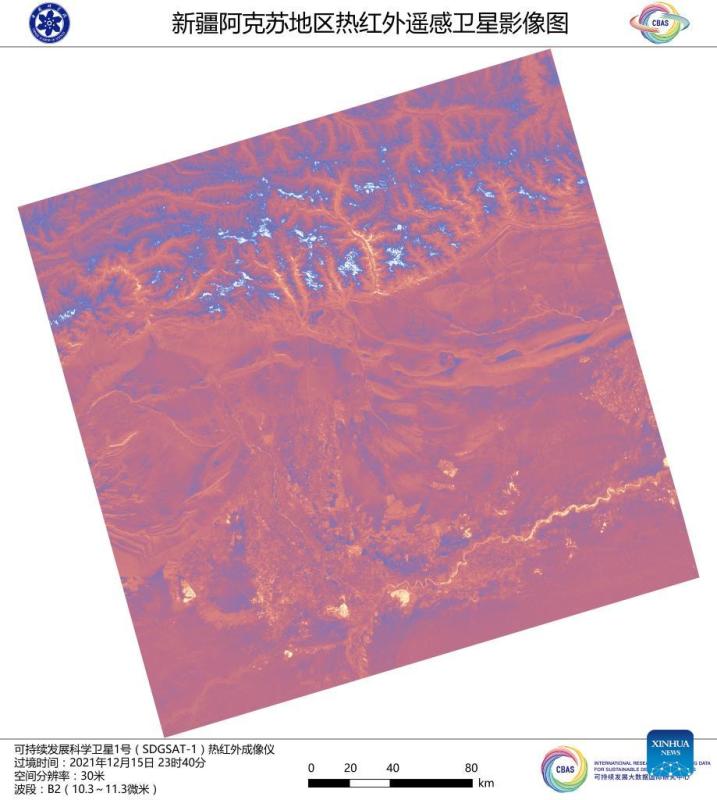
Image captured by the satellite SDGSAT-1 shows a view of Aksu Prefecture in northwest China's Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. China's recently launched Earth science satellite has sent back its first remote sensing images, according to its developer, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Using thermal infrared, low light level and multispectral imagers, the satellite captured images of multiple cities and regions, including Beijing, Shanghai, the Yangtze River Delta, Lake Namtso in Tibet, Aksu Prefecture in Xinjiang, and Paris in France. The satellite SDGSAT-1 is the world's first space science satellite dedicated to serving the U.N. 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The satellite was launched into space on Nov. 5. (Chinese Academy of Sciences/Handout via Xinhua)
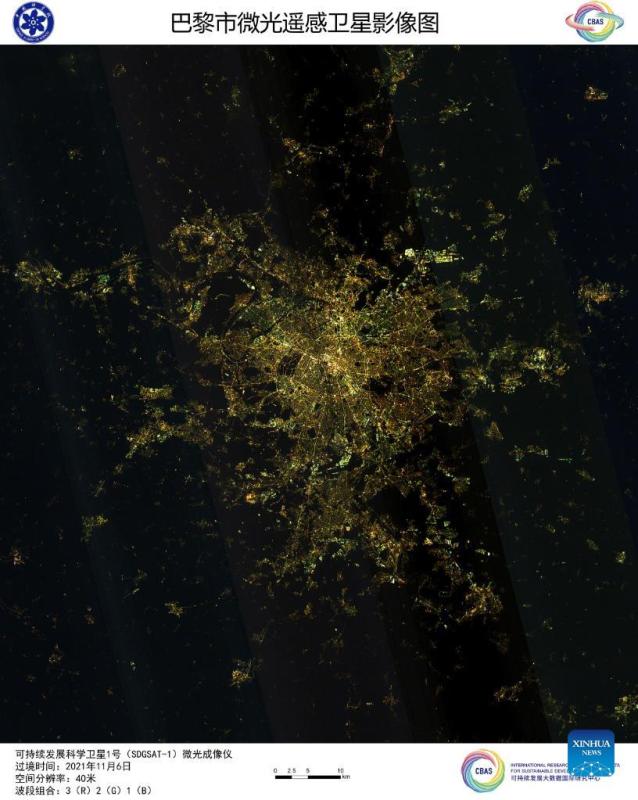

Image captured by the satellite SDGSAT-1 shows a view of Paris in France. China's recently launched Earth science satellite has sent back its first remote sensing images, according to its developer, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Using thermal infrared, low light level and multispectral imagers, the satellite captured images of multiple cities and regions, including Beijing, Shanghai, the Yangtze River Delta, Lake Namtso in Tibet, Aksu Prefecture in Xinjiang, and Paris in France. The satellite SDGSAT-1 is the world's first space science satellite dedicated to serving the U.N. 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The satellite was launched into space on Nov. 5. (Chinese Academy of Sciences/Handout via Xinhua)
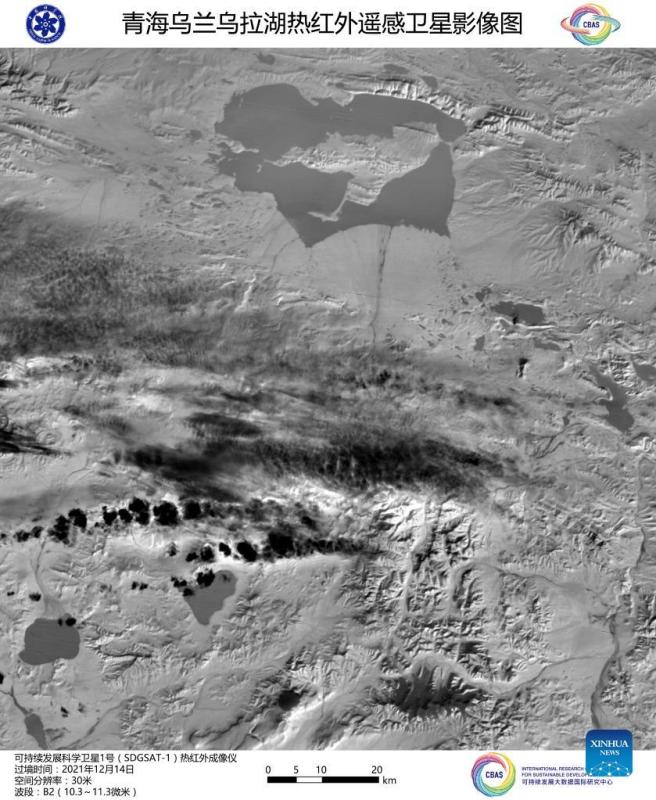

Image captured by the satellite SDGSAT-1 shows a view of Ulan Ul Lake in northwest China's Qinghai Province. China's recently launched Earth science satellite has sent back its first remote sensing images, according to its developer, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Using thermal infrared, low light level and multispectral imagers, the satellite captured images of multiple cities and regions, including Beijing, Shanghai, the Yangtze River Delta, Lake Namtso in Tibet, Aksu Prefecture in Xinjiang, and Paris in France. The satellite SDGSAT-1 is the world's first space science satellite dedicated to serving the U.N. 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The satellite was launched into space on Nov. 5. (Chinese Academy of Sciences/Handout via Xinhua)
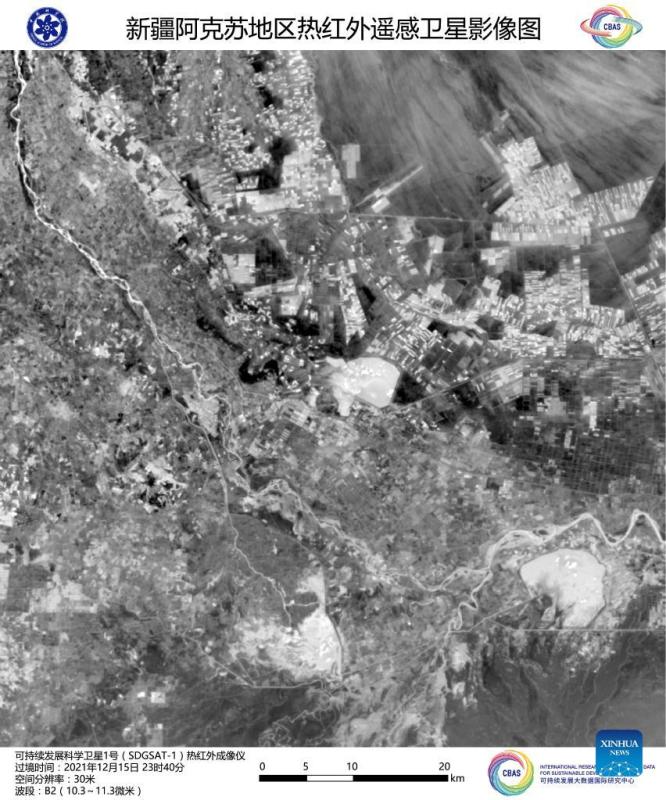

Image captured by the satellite SDGSAT-1 shows a view of Aksu Prefecture in northwest China's Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. China's recently launched Earth science satellite has sent back its first remote sensing images, according to its developer, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Using thermal infrared, low light level and multispectral imagers, the satellite captured images of multiple cities and regions, including Beijing, Shanghai, the Yangtze River Delta, Lake Namtso in Tibet, Aksu Prefecture in Xinjiang, and Paris in France. The satellite SDGSAT-1 is the world's first space science satellite dedicated to serving the U.N. 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The satellite was launched into space on Nov. 5. (Chinese Academy of Sciences/Handout via Xinhua)

Image captured by the satellite SDGSAT-1 shows a view of east China's Shanghai. China's recently launched Earth science satellite has sent back its first remote sensing images, according to its developer, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Using thermal infrared, low light level and multispectral imagers, the satellite captured images of multiple cities and regions, including Beijing, Shanghai, the Yangtze River Delta, Lake Namtso in Tibet, Aksu Prefecture in Xinjiang, and Paris in France. The satellite SDGSAT-1 is the world's first space science satellite dedicated to serving the U.N. 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The satellite was launched into space on Nov. 5. (Chinese Academy of Sciences/Handout via Xinhua)

Image captured by the satellite SDGSAT-1 shows a view of Beijing, capital of China. China's recently launched Earth science satellite has sent back its first remote sensing images, according to its developer, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Using thermal infrared, low light level and multispectral imagers, the satellite captured images of multiple cities and regions, including Beijing, Shanghai, the Yangtze River Delta, Lake Namtso in Tibet, Aksu Prefecture in Xinjiang, and Paris in France. The satellite SDGSAT-1 is the world's first space science satellite dedicated to serving the U.N. 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The satellite was launched into space on Nov. 5. (Chinese Academy of Sciences/Handout via Xinhua)
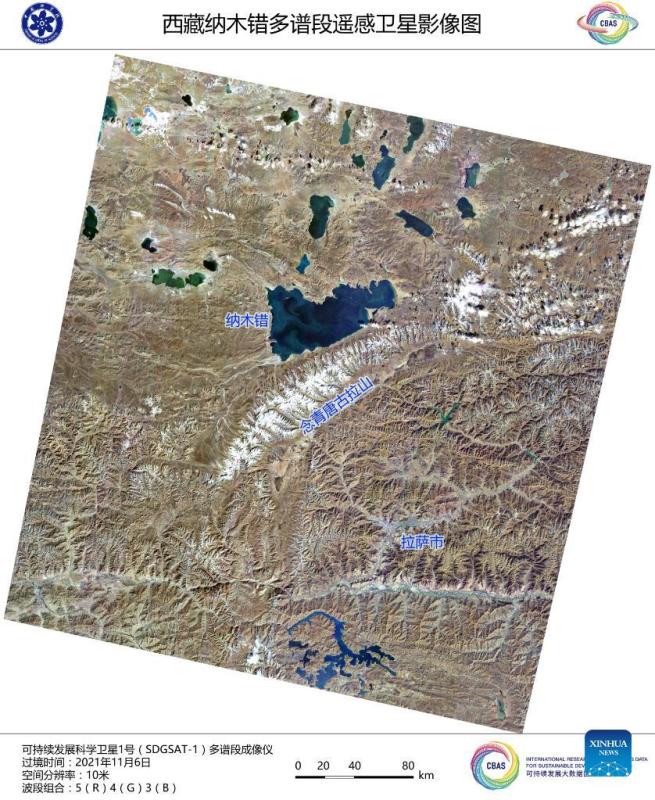

Image captured by the satellite SDGSAT-1 shows a view of Lake Namtso in southwest China's Tibet Autonomous Region. China's recently launched Earth science satellite has sent back its first remote sensing images, according to its developer, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Using thermal infrared, low light level and multispectral imagers, the satellite captured images of multiple cities and regions, including Beijing, Shanghai, the Yangtze River Delta, Lake Namtso in Tibet, Aksu Prefecture in Xinjiang, and Paris in France. The satellite SDGSAT-1 is the world's first space science satellite dedicated to serving the U.N. 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The satellite was launched into space on Nov. 5. (Chinese Academy of Sciences/Handout via Xinhua)






























 京公網安備 11010202009201號] [京ICP備05004340號-1]
京公網安備 11010202009201號] [京ICP備05004340號-1]